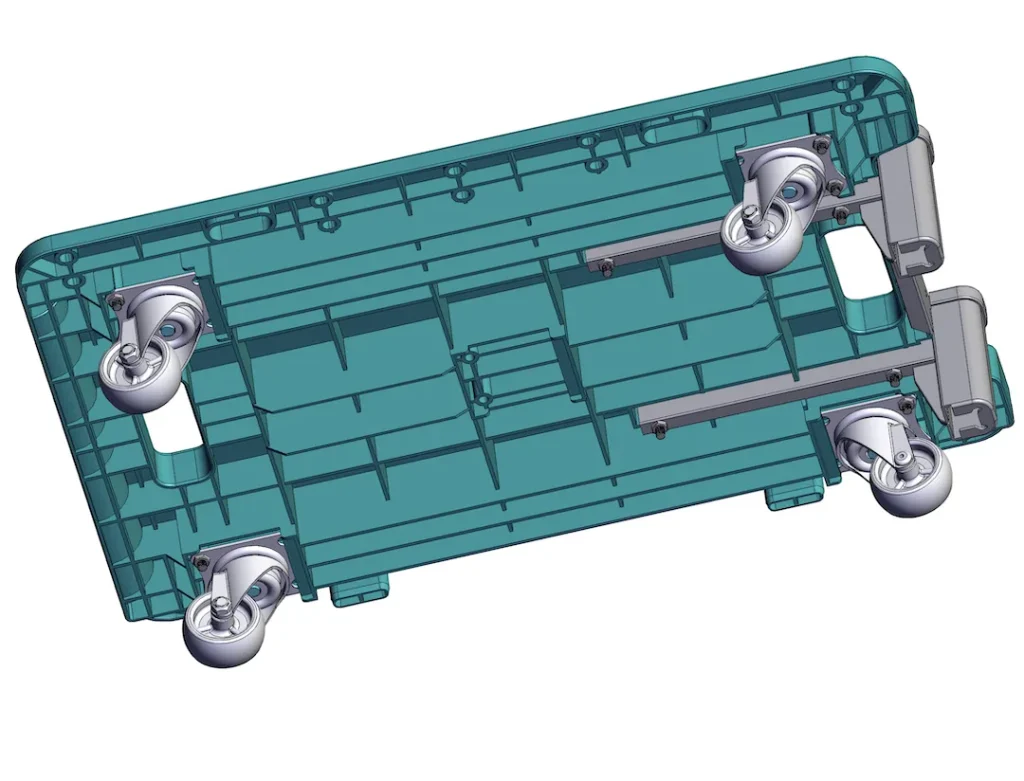
Able Hardware builds welded industrial carts that roll safely, quietly, and for a long service life. This page shows how to choose the right casters and load ratings—and how our factory engineers integrate those choices into a robust, export-ready cart structure.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Engineering Ontology for Caster Selection
Entities & Taxonomy
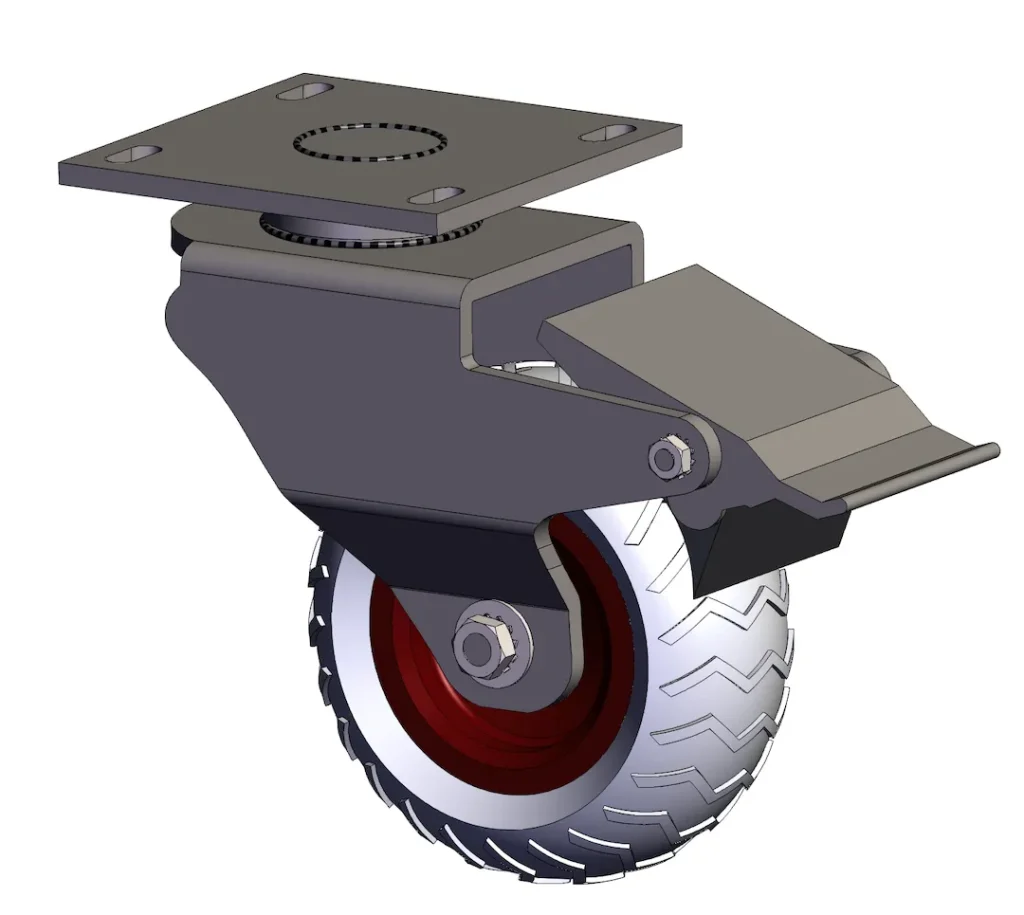
- Caster Assembly → bracket (swivel/rigid, kingpin/kingpinless), wheel, Lager, axle, Bremse (total/side/threaded stem options), fasteners.
- Radmaterialien → polyurethane (PU), Gummi (NR/SBR), thermoplastic rubber (TPR), nylon/PA6, phenolic, cast iron/steel, high-temp compounds.
- Bearing Types → plain/bushing, roller, precision ball, tapered roller, sealed stainless for washdown.
- Montageschnittstellen → top plate (bolt pattern), weld-on plate, stem (threaded/expanding), custom interface blocks.
- Cart Frame → base weldment, cross-members, Zwickel, mounting pads, beenden (Pulvermantel, Zink, E-Coat).
Key Properties
- Load rating (statisch/dynamisch), wheel diameter (Ø100–Ø250 mm typical), tread width, durometer (Shore A), swivel offset, kingpin design, brake torque, temperature range, chemische Resistenz, ESD, noise, floor protection, washdown rating.
Relationships (Design Rules of Thumb)
- Floor type ↔ tread: brittle/finished floors → soft PU/TPR; rough concrete → tougher PU/nylon; hot debris/metal chips → phenolic/iron.
- Environment ↔ bearing: washdown/food → sealed stainless; dusty/shock → roller or kingpinless with impact bushings.
- Speed/Duty ↔ dynamic rating: higher speeds and continuous duty require derating and precision bearings.
- Cart geometry ↔ caster set-up: long loads often use 6-caster layouts (2 rigid center + 4 swivel corners) for tracking and maneuverability.
- Weld class/finish ↔ longevity: frame stiffness, ISO 5817 Schweißqualität, and coating thickness determine bolt-hole integrity and anti-corrosion performance. Sehen /standards/iso-5817/.
Load Rating Math (Simple and Safe)
Step 1 — Total Mass
Add payload mass plus cart mass. Beispiel: Nutzlast 600 kg + cart 80 kg = 680 kg.
Step 2 — Safety Factor
Wählen 1.3–2,0 depending on shocks, floor joints, ramps, and handling method. (Higher for impacts, forklifts pushing carts, or uneven floors.)
Step 3 — Effective Casters
On real floors, assume only three casters carry load at any time on a four-caster cart. Per-caster required rating = (Total mass × Safety factor) ÷ Effective casters.
Beispiel: 680 kg × 1.5 ÷ 3 = 340 kg per caster minimum dynamic rating. Choose the next rating up (z.B., 400–450 kg per caster) to add margin for wear and speed.
Speed & Duty Cycle
As travel speed rises (z.B., >4 km/h) and duty becomes continuous, heat builds in the tread and grease, reducing dynamic capacity. Derate by 10–30% or move to larger diameter wheels, precision ball bearings, and tougher treads.
Wheel Material Selection
Polyurethane (PU)
- Use when: you need quiet rolling, floor protection, and high capacity.
- Notes: select lower Shore A for tiles/epoxy floors; higher durometer for concrete and higher loads.
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) / Gummi
- Use when: maximizing low noise and shock absorption.
- Notes: lower capacity than PU; avoid oil-saturated areas for natural rubber.
Nylon (PA6)
- Use when: you want low rolling resistance, chemische Resistenz, and easy washdown.
- Notes: noisy on joints; can flat-spot under static loads; good for cold rooms.
Phenolic / Composite
- Use when: high temp or chip-laden floors.
- Notes: hard on floors; verify temperature curve for ovens/bake lines.
Cast Iron / Stahl
- Use when: extreme loads and hot/abrasive conditions.
- Notes: no floor protection; pair with steel plates or sacrificial tracks.
Bearings, Klammern & Mounting
Bearing Choice
- Plain/Bushing: impact-tolerant, simple; higher push force.
- Roller: good for heavy loads at low-moderate speed.
- Precision Ball: lowest push force and best at higher speed; seal for washdown.
Swivel vs Rigid
- All swivel (4x): tight spaces, but can “crab.”
- 2 schwenken + 2 starr: easiest tracking over distance.
- 6-caster sets: center rigid pair + swivel corners for long frames.
Mounting Patterns & Frame Integration
Verwenden top plates with bolt patterns sized to load; hinzufügen welded reinforcement pads to spread stress. Our frames include CNC-cut mounting holes und robotic MIG fillet welds to hold plate flatness and torque. See our process pages: /services/automatic-welding/ und /services/laser-cutting-cnc-machining/.
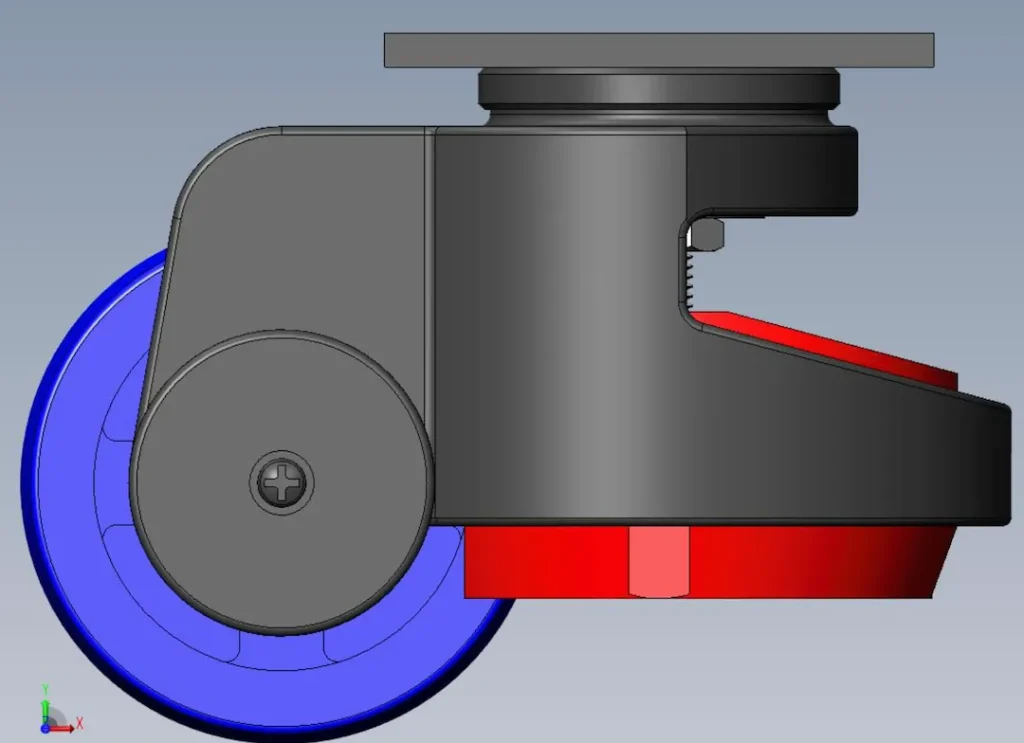
Typical Specifications We Build To
- Wheel diameters: Ø100–Ø200 mm standard; Ø250 mm for ramps/obstacles.
- Per-caster dynamic rating: 150–800 kg typical; heavy-duty upon request.
- Tread hardness: 85–98 Shore A PU; soft grades for epoxy floors.
- Swivel radius: optimized to maintain turning clearance with skirts and bumpers.
- Beenden: powder coat 60–90 μm or zinc + powder system for coastal use. Sehen /services/powder-coating/.
Cost Drivers (What Moves the Price)
- Radmaterial & Größe: larger Ø and premium PU compounds increase cost.
- Bearing type: precision ball bearings cost more but reduce push force (operator fatigue).
- Bracket design: kingpinless and sealed swivel heads for shock duty add cost.
- Frame reinforcement: thicker mounting pads and gussets for high-impact sites.
- Finish system: duplex coatings and pre-treatments for corrosion class C3–C5. Expect tiered ranges based on load class and environment; we quote with options to balance life-cycle cost vs. unit cost.
RFQ-Checkliste (Faster, Safer Sourcing)
- Payload mass und cart mass.
- Number of casters and layout (4, 6, or custom).
- Floor condition (Epoxidharz, tiles, rough concrete, ramps, thresholds).
- Speed & Pflicht (manual push, Schlepper, distance per shift).
- Umfeld (washdown, oils, Chips, temperature).
- Mounting pattern (plate size/bolt pitch) und deck clearances.
- Brake/lock braucht (total lock, directional lock).
- Beenden (powder coat color, Zink + Pulver, stainless hardware).
Upload your drawing and get a quote now → STEP/IGES/DWG/PDF welcome. Verwenden: /products/welding-trolley-carts/ or contact via /resources/engineering/.
Warum Able-Hardware
China-based OEM/ODM factory mit Automatische/Robotermig Schweißen, Präzision CNC laser cutting, and export QA. We design casters into the structure—bolted interfaces, weld pads, and coatings—so your carts roll to spec from day one. Erkunden: /products/custom-metal-frames/.

FAQ
What wheel materials do you recommend for epoxy or tiled floors?
Polyurethane (lower Shore A) or TPR to protect finishes and reduce noise; pair with precision ball bearings for easy push.
What processes do you use for the cart frame?
Laser schneiden, CNC forming, und Automatische/Robotermig welding with calibrated parameters; TIG is available for stainless or thin-gauge parts. Sehen /services/automatic-welding/.
What tolerances can you hold on caster mounting pads?
Typical flatness ≤0.5 mm over 200 mm pad; hole position ±0.25 mm from CNC cutting. Tighter tolerances available with machining.
What weld class do you meet?
Weld quality evaluated to ISO 5817 (B or C per project). Sehen /standards/iso-5817/.
What coatings are available?
Standard powder coat 60–90 μm; duplex zinc + powder for coastal or chemical exposure; stainless hardware upon request. Sehen Pulverbeschichtung.
What are your MOQ and lead times?
MOQs are flexible (pilot lots welcome). Typical lead time 15–30 days after drawing approval, depending on complexity and coating cure schedules.
What drawings do you need for a quotation?
2D with critical dimensions + 3D STEP/IGES, load case notes, Bodentyp, caster material preference, beenden, and any test/inspection requirements.
Aufruf zum Handeln
Ready to spec your casters? Upload your drawing and application notes, and our engineers will return a load calculation, caster shortlist, and structural proposal.