Inhaltsverzeichnis
What Are Tugger Carts?
Tugger carts are towable carts for tugger trains, improving material flow and reducing internal traffic. Able Hardware manufactures custom OEM/ODM tugger carts in China, auf Ihre Last abgestimmt, Route, and coupling specs, with export-ready QA.
Tugger Carts vs. Push Carts vs. Gabelstapler (When to Use Each)
Use tugger carts when you need repeatable routes, higher throughput, and safer, forklift-light operations. Push carts are best for short distances and low-frequency moves. Forklifts remain ideal for pallet handling, high stacking, or irregular routes—while tugger trains excel at scheduled replenishment and WIP movement with less congestion.
Common Industries and Workflows (Line Feeding, Kitting, Nachschub, In Bearbeitung)
Typical applications include line feeding (kanban loops), kitten, supermarket replenishment, WIP transfer between cells, and finished-goods movement. If your operation already uses an Industriewagen fleet, tugger carts are a natural upgrade for route-based towing and multi-stop delivery.
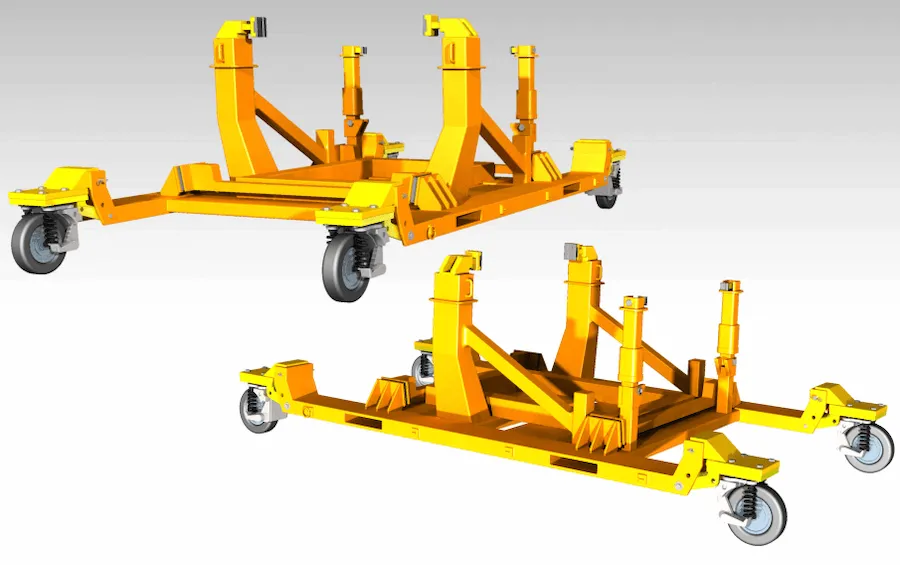
Tugger Cart Types and Configurations
Center-Steer Tugger Carts
Center-steer designs offer predictable tracking and stable towing for general factory routes. They’re a strong choice when you want a balance of maneuverability and simplicity.
Dual-Steer Tugger Carts
Dual-steer configurations enhance control through corners and transitions. They are commonly selected for tighter aisles or when multiple carts must follow consistent paths.
Quad-Steer Tugger Carts (High Maneuverability)
Quad-steer designs maximize turning performance in tight spaces and complex routes. They’re ideal for compact workcells, dense racking zones, and frequent directional changes.
Rear-Steer / Tongue-and-Hitch Tugger Carts
Rear-steer tongue-and-hitch carts are a classic, cost-effective approach for straightforward towing. They’re popular where coupling standards are already defined across sites.
Mother–Daughter Tugger Cart Systems
Mother–daughter systems support efficient drop-off and pick-up: a mother cart tows multiple daughter carts that can be staged at work areas. This setup is excellent for high-mix production and multi-point delivery.
Towable Warehouse Trailers (Push-or-Pull Use)
Hybrid towable trailers can be pushed locally and towed in trains for longer routes—useful when operators need flexible handling at the destination.
Pallet Tugger Carts (Pallet & Container Transfer)
Pallet-oriented tugger carts are built to carry pallet footprints or pallet-like unit loads, often with guides, stops, or capture features to stabilize loads on corners.
Conveyor-Top / Roller-Top Tugger Carts
Roller-top or conveyor-top tugger carts streamline line feeding by enabling easy transfer onto flow racks or workstations—especially effective for totes, Kartons, and containers.
Tilt Tugger Carts (Dump / Tilt Options)
Tilt functions help with ergonomic unloading of parts bins or scrap handling. Options may include controlled tilt angles and assisted lift/tilt mechanisms.
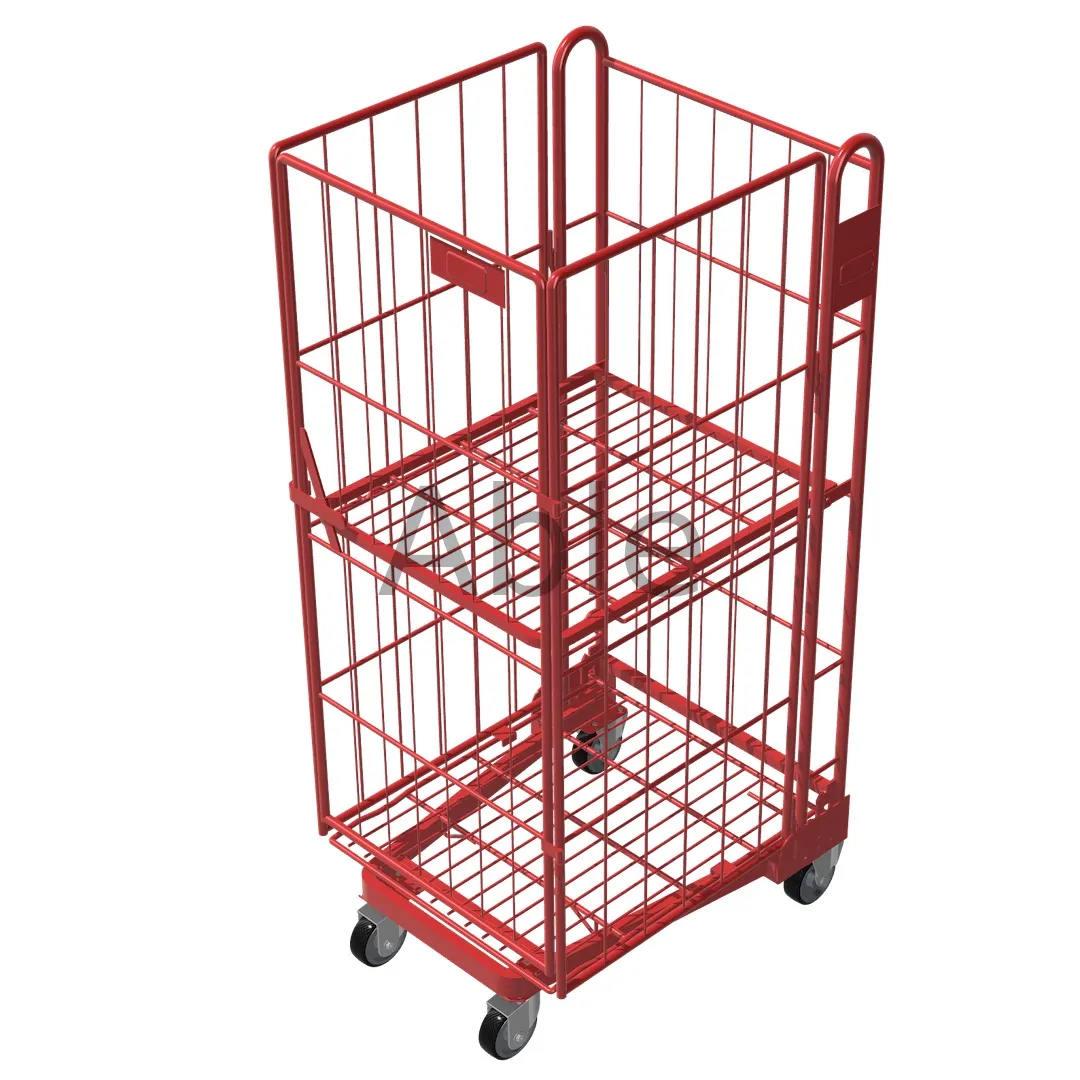
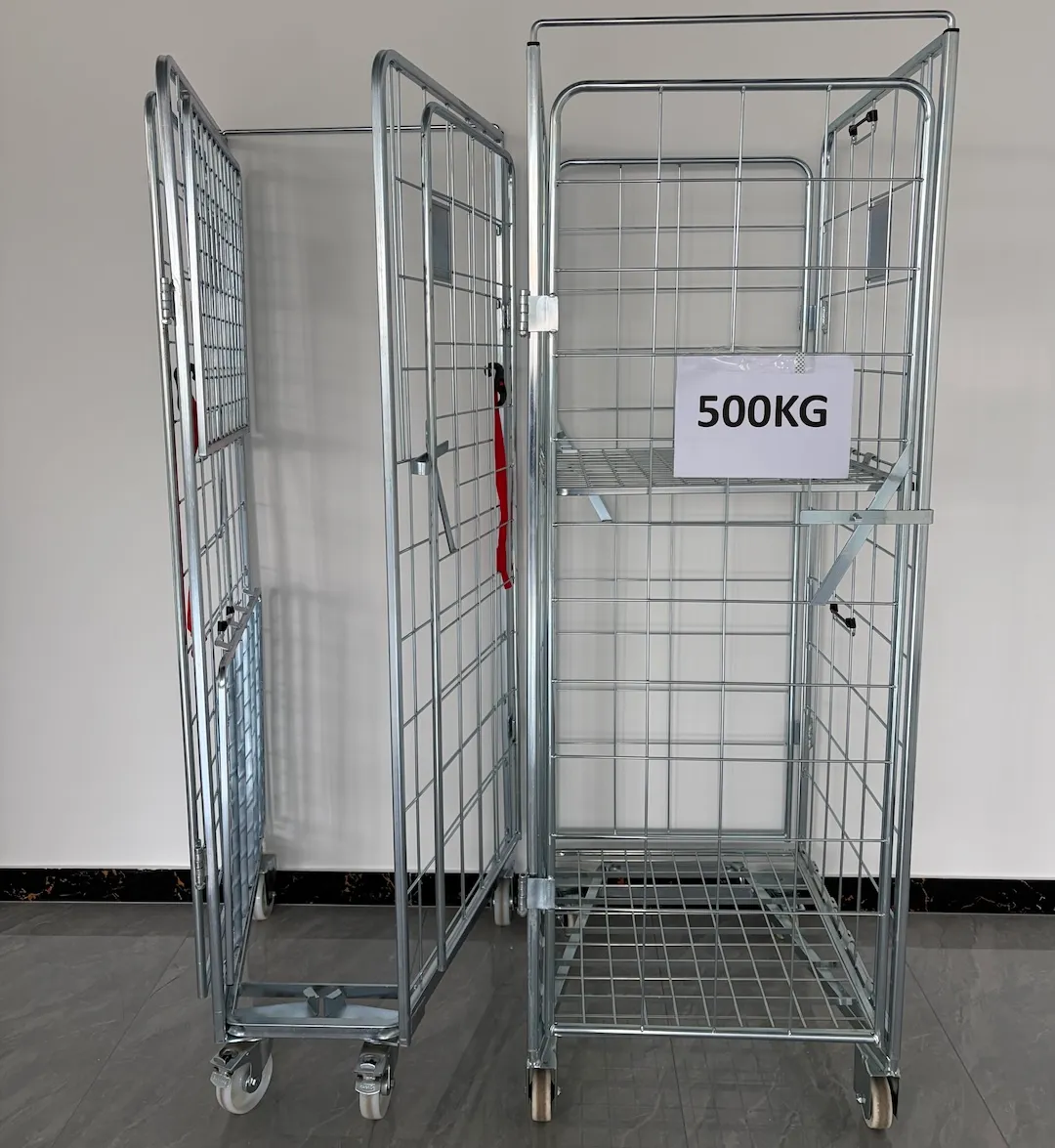
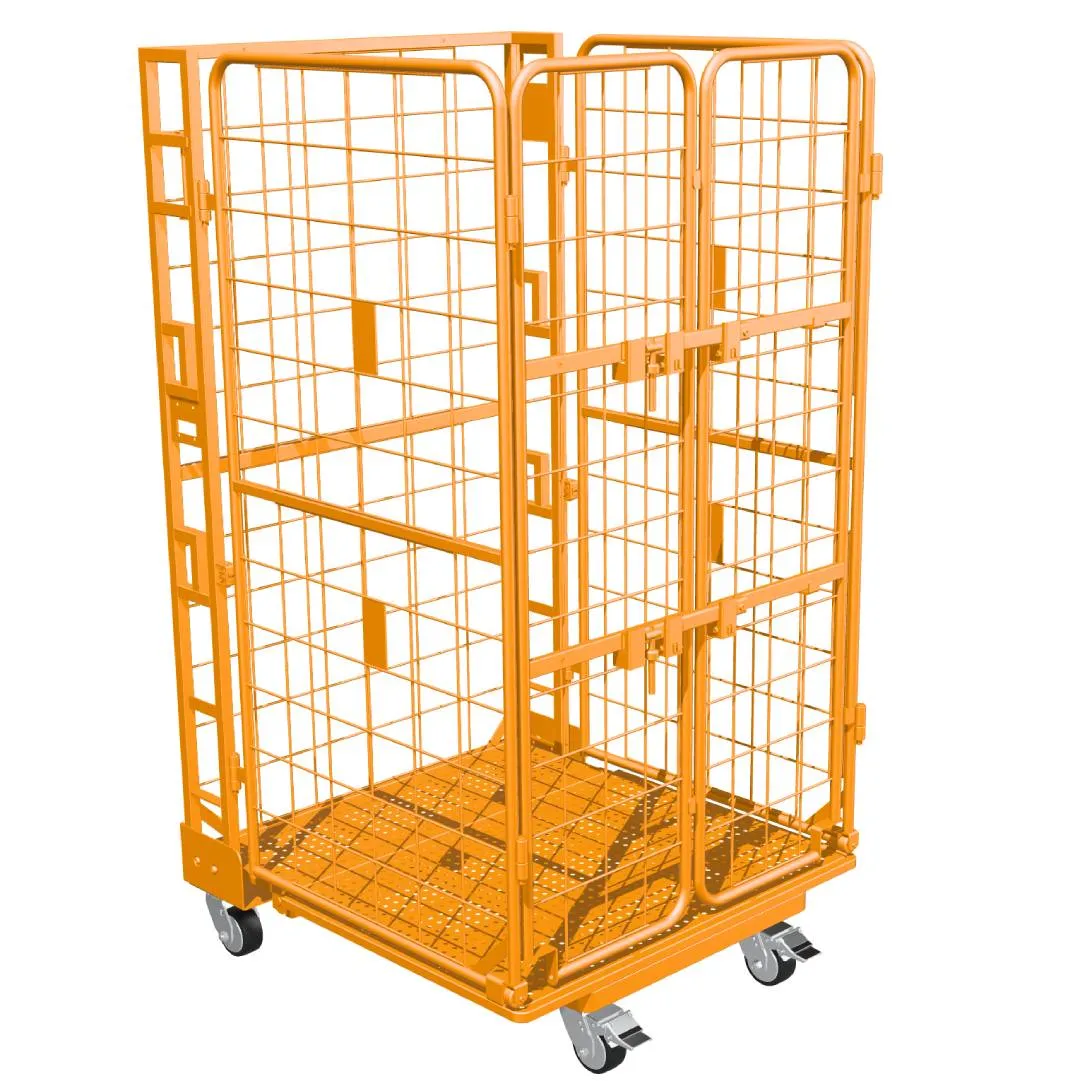
Towable Security Cage Tugger Carts (Lockable / Mesh)
Lockable cage-style tugger carts protect high-value inventory and tools in transit. For higher security storage and distribution, consider integrating designs similar to a Logistischer Rollkäfigwagen.

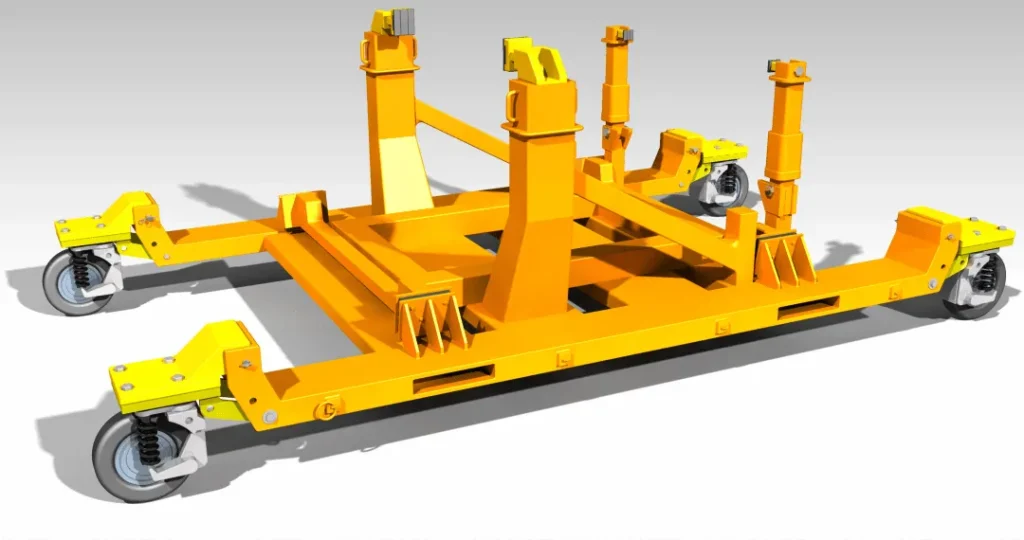
Key Components of a Tugger Cart System
Frame and Load-Bearing Structure
The frame is the backbone of towing performance. We engineer stiffness, weld layout, and reinforcement to control deflection and maintain stable tracking—especially for long trains and dynamic loads. Many designs share proven architecture with our geschweißte Stahlrahmen for industrial duty.
Tow Bar, Drawbar, Tongue, and Hitch Options
We build to your tow height, pin style, hitch geometry, and safety preferences. Standardization here is critical—consistent coupling reduces downtime and improves operator confidence.
Steering Linkage and Tracking Behavior
Steering geometry determines how well carts follow the tugger (and each other). Our engineering focuses on cornering behavior, off-tracking control, and repeatable follow-the-leader movement.
Räder, Rollen, Bremsen, and Directional Locks
Radmaterial, Durchmesser, Lager, and caster layout directly affect rolling resistance, noise, and stability. Brakes and directional locks are specified based on route slopes, stop distance requirements, und Sicherheitsregeln.
Deck Styles: Wohnung, Pallet Interface, Roller, and Custom Tops
From flat decks to pallet capture and roller tops, the load interface is tailored to how materials are picked up, carried, and transferred at each station.
Sicherheitsvorrichtungen: Stoßstangen, Guards, Etiketten, and Load Stops
Options include perimeter bumpers, Eckwächter, toe protection, load stops, and clear ID/label plates—supporting safer movement in shared pedestrian environments.
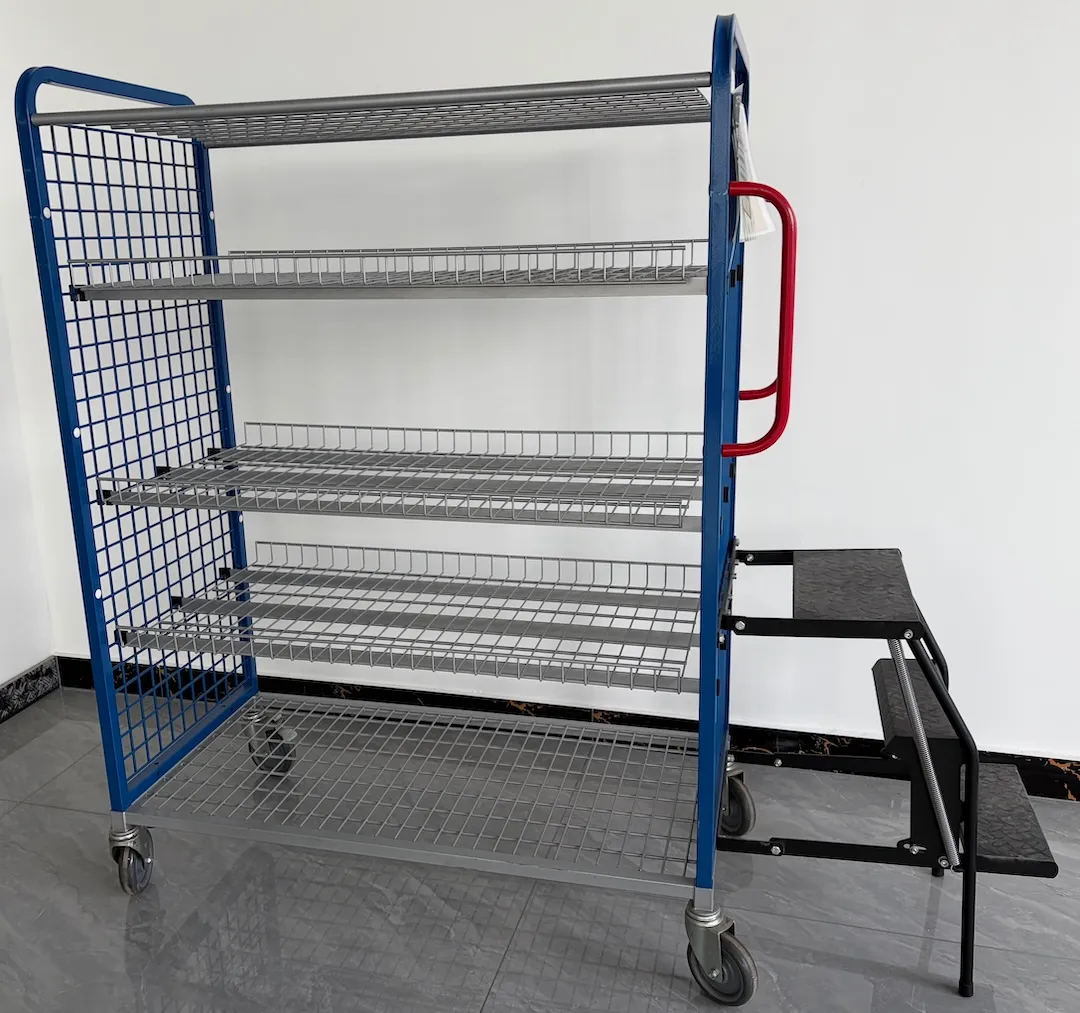
Accessories: Regale, Teiler, Bin Rails, Haken, ID Plates
Add-ons such as shelves, Trennwände, bin rails, hooks, document holders, and barcode plates help standardize kits and reduce handling errors. If your workflow includes mixed cart styles, you may also use a Zusammenklappbarer Logistikwagen at endpoints for compact staging.
Performance Specifications That Matter
Belastbarkeit: Static vs. Dynamic Capacity
Dynamic capacity (in motion) matters most for tugger systems. We size the frame, tow points, and wheel sets to match dynamic forces in corners, starts/stops, and uneven floors.
Turning Radius and Aisle Width Requirements
Turning radius, wheelbase, and steering type must match aisle widths and station clearances. Tight aisles often favor quad-steer or optimized dual-steer geometry.
Tracking Accuracy (How Well Carts Follow the Tugger)
Tracking performance reduces aisle interference and product damage. We tune coupling and steering geometry to minimize off-tracking—especially for long trains.
Speed Limits and Stability in a Train
Train stability depends on load height, center of gravity, wheel choice, and braking strategy. We recommend speed limits based on route conditions and safety policies.
Floor Conditions: Concrete, Epoxy, Grating, and Mixed Surfaces
Floor type affects wheel selection and rolling resistance. We can specify wheels for epoxy, concrete joints, dock plates, or mixed indoor routes.
Noise Control and Rolling Resistance (Wheel Material Choices)
Noise and push/pull effort are improved through wheel compound selection and bearing choices—important for operator comfort and long shifts.
Durability Targets: Cycle Life, Auswirkungen, and Wear Points
High-cycle areas include tow points, steering joints, caster mounts, and bumpers. We reinforce and validate these points during prototyping to hit durability goals.
How to Choose the Right Steering Type
How Center-Steer Handles Corners
Center-steer provides stable tracking on standard turns and is often the simplest path to dependable performance.
When Dual-Steer Improves Control
Dual-steer is preferred when aisles are narrow or when carts must navigate tighter turns without excessive off-tracking.
Why Quad-Steer Works in Tight Aisles
Quad-steer maximizes maneuverability and can reduce corner interference in high-density layouts.
Train Length, Cornering, and “Off-Tracking” Considerations
Longer trains amplify off-tracking and braking distance. We help you define practical train length, coupling spacing, and steering strategy to meet safety and flow targets.
Tow Interface and Coupling Design
Tongue-and-Hitch Standards (Geometrie, Pin, Höhe)
Define a consistent tow height and pin/hitch standard across your fleet. This improves interchangeability and reduces operator errors.
Drawbar Length and Coupling Spacing for Safe Cornering
Spacing affects corner behavior and train stability. We optimize drawbar length for your route geometry and station clearances.
Multi-Point Coupling for Train Flexibility
Multi-point coupling supports flexible train lengths and faster reconfiguration—useful for mixed-SKU lines and seasonal demand changes.
Parking Stands and Tow Bar Storage
Parking stands and tow bar storage reduce trip hazards and protect couplers from impact damage during staging.
Pallet and Container Handling Options
Pallet Deck vs. Pallet Capture (Stops, Guides, Chocks)
Pallet capture features (stops, Führer, chocks) improve load retention and cornering stability, especially when routes include ramps or floor transitions.
Container Carts for Totes, Mülleimer, and Bulk Boxes
Container-focused tops can be configured for standard totes, Drahtkörbe, or bulk boxes—ideal for replenishment loops.
Roller-Top Carts for Flow Racks and Line Feeding
Roller-top carts speed transfers into flow racks and workstations, reducing manual lifting and improving takt-time consistency.
Lift / Tilt Options (Pneumatic or Hydraulic Assist)
Assisted lift/tilt options support ergonomic unloading and safer handling of heavy parts containers.
Sicherheit, Ergonomie, and Workplace Compliance
Braking Strategy for Trains (Where to Place Brakes)
Braking can be applied on selected carts or at defined intervals based on route risk and stop-distance needs. We design mounts for reliable brake performance.
Anti-Kipp-Design: Center of Gravity and Wheelbase
We manage stability through wheelbase design, load height guidance, and structural stiffness—reducing tip risk during turns and sudden stops.
Push/Pull Force Targets and Operator Fatigue
Lower rolling resistance and smart handle/coupler design reduce operator fatigue, especially for hybrid push-and-pull scenarios.
Visibility, Corner Protection, and Pedestrian Safety
Add bumpers, high-visibility markers, and corner guards to protect people and product in shared lanes.
Load Labels, Warnings, and Identification Plates
Clear labels improve compliance and reduce misuse. We can add serialized ID plates and barcode locations to match your asset tracking.
Materialien und Oberflächenveredelungen
Carbon Steel vs. Rostfreier Stahl (When Each Makes Sense)
Carbon steel is cost-effective for indoor use; stainless steel is selected for corrosion resistance, washdown, or hygienic areas.
Powder Coating vs. Zinc Plating (Durability Trade-Offs)
Powder coating fits indoor routes and branding colors; zinc plating supports more demanding corrosion conditions. We’ll recommend the best fit for your environment and lifecycle expectations.
Corrosion Resistance for Humid or Washdown Areas
For humid, wet, or washdown use, we specify materials and finishes to protect critical joints and wear areas.
Low-Temperature Considerations for Cold Rooms / Freezers
Low temperatures change wheel performance and coating behavior. We can tailor wheel compounds and finishes for cold-room stability.
Optional ESD-Safe Wheels and Grounding (If Needed)
For ESD-sensitive zones, we can specify ESD-safe wheels and grounding solutions to align with your handling protocols.
Customization and OEM Engineering Service
Your RFQ Checklist (Zeichnungen, Laden, Route, Umfeld, Menge)
Share your target load (kg), cart envelope size, tow standard, route details (Gangbreite, corners, ramps), Umgebung, und Jahresvolumen. If you also use Bestückung von Kommissionierwagen in the same workflow, include how items transfer between carts.
Concept-to-CAD: Layout Optimization for Your Workflow
We convert your requirements into CAD-ready designs and recommend steering/coupling configurations for tracking and safety.
Schnelles Prototyping: What Can Be Validated in a Sample
Prototypes validate tracking, drehen, braking, tow interface fit, Ergonomie, and key load behavior—before you scale to production.
DFM Review and Design Iteration (ECN / Change Control)
We support engineering changes with controlled revisions so your approvals and documentation stay aligned across prototype, pilot, and mass production.
Branding and Identification (Logoplatten, Farben, Barcodes)
Add branded colors, Logoplatten, barcode plates, and standardized labeling to match your internal systems and 5S goals.
Nestbar / Stapelbar / KD Packaging Design for Shipping
We design for nesting, stacking, or knock-down packing to reduce freight cost and improve container utilization.
Herstellung: How Tugger Carts Are Built (Chinese OEM with Robotic Welding)
Robotic Automatic Welding for Repeatable Frame Geometry
Our production is built around repeatable fabrication for consistent geometry and stable towing performance. For buyers needing advanced welding capability, siehe unsere Automatisierte Roboterschweißdienste.
Laser schneiden, Biegen, and Fixture-Controlled Assembly
Laser cutting and bending create accurate parts; fixtures control assembly alignment to keep steering and coupler geometry consistent.
Critical Weld Points: Tow Nodes, Steering Arms, and Cross Bracing
Tow nodes, steering mounts, and cross braces are treated as critical-to-performance areas, reinforced to handle dynamic loads.
Surface Treatment and Curing Control (Beschichtungsdicke)
Coating selection and thickness targets are matched to your corrosion needs and wear expectations.
Final Assembly: Räder, Bremsen, Anhängerkupplungen, and Accessories
We assemble and verify wheel sets, Bremsen, couplers, and accessories to ensure fit and function.
Qualitätskontrolle: Maßprüfungen, Weld Inspection, Load Tests
Every project includes defined checkpoints and documentation aligned to your requirements—supported by our export-ready Qualitätskontrolle Verfahren.
Kosten, Price Drivers, und Vorlaufzeit
What Affects Tugger Cart Cost (Struktur, Steering, Coupling, Optionen)
Cost is driven by frame complexity, steering type, coupler standardization, wheel/brake specification, and accessory requirements.
Steering Complexity: Center vs. Dual vs. Quad (Cost Implications)
Quad-steer and specialized steering linkages typically increase part count and assembly time, while center-steer is often the most economical.
Material and Finish Choices (Powder Coat vs. Zinc vs. Rostfrei)
Stainless and higher corrosion finishes raise material and process costs; powder coat is usually the most cost-efficient for indoor use.
Wheels and Brakes (Performance vs. Budget)
Higher-performance wheels and braking systems reduce noise and effort but may increase unit cost—often worth it for high-cycle routes.
Prototype Cost vs. Production Cost (How to Reduce Total Cost)
Prototypes are an investment to confirm performance early. Standardizing couplers, reducing unique parts, and designing for nesting/KD packing can reduce total landed cost.
MOQ, Werkzeuge, and Fixture Costs (When They Apply)
Simple designs may require minimal tooling; more complex steering or repeated high-volume projects can justify dedicated fixtures for better repeatability.
Typical Lead Times: Prototyp, Pilot Run, Mass Production
Die Vorlaufzeit hängt von der Komplexität ab, beenden, and testing requirements. We provide realistic schedules after RFQ review and drawing confirmation.
FAQ
What’s the difference between tugger carts and tugger trains?
A tugger cart is one towable unit; a tugger train is multiple carts coupled together behind a tugger.
How many carts can one tugger pull safely?
It depends on total dynamic load, route slope, braking strategy, und Sicherheitsregeln. We can help estimate train limits from your route data.
Should I choose center-steer, dual-steer, or quad-steer?
Choose based on aisle width, turn geometry, tracking accuracy needs, and budget. Tight aisles and complex routes often benefit from dual- or quad-steer.
Can tugger carts handle pallets and containers on the same train?
Yes—mixed trains are common when couplers and heights are standardized and load interfaces are designed for safe transitions.
What wheel material is best for epoxy floors or rough concrete?
Epoxy often favors low-noise, floor-friendly wheels; rough concrete may need tougher tread and larger diameter. Provide floor details and we’ll recommend options.
Do I need brakes on every cart in a train?
Not always. Brake placement depends on route risk and required stopping distance.
Can you make nestable or knock-down designs to save shipping cost?
Yes—nesting and KD designs can significantly reduce freight per unit.
What documents can you provide for QA and inspection?
Typical documents include dimensional reports, inspection checklists, and material traceability—aligned with your QA requirements.
What is the usual prototype lead time and what do you need from us?
Provide load (kg), Maße, route details, tow standard, Umgebung, and quantity targets. We’ll confirm a prototype plan and schedule with your team.
Can you customize tow height, hitch type, and coupling geometry?
Yes—tow standards are a core customization area, and we design to match your tugger and fleet requirements.
Aufruf zum Handeln
Send your RFQ to Able Hardware—we’ll reply with an engineered proposal, fast prototype plan, and a production quote range.
Please include: Belastbarkeit (kg), Gesamtabmessungen, steering type (center/dual/quad), tow interface (height/pin/hitch), route details (aisle width/turns/ramps), Bodentyp, finish requirement, and target order quantity.
Fordern Sie ein Angebot an
Mehr Industriewagen:






